Thunderbolt controllers multiplex one or more individual data lanes from connected PCIe and DisplayPort devices for transmission via one duplex Thunderbolt lane, then de-multiplex them for consumption by PCIe and DisplayPort devices on the other end.
| Pin Number |
Pin Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | HPD | Hot plug detect |
| 3 | HS0TX+ | HighSpeed transmit 0 (positive) |
| 4 | HS0RX+ | HighSpeed receive 0 (positive) |
| 5 | HS0TX- | HighSpeed transmit 0 (negative) |
| 6 | HS0RX- | HighSpeed receive 0 (negative) |
| 7,8 | GND | Ground |
| 9 | LSR2P TX | LowSpeed transmit |
| 10 | GND | Ground (reserved) |
| 11 | LSP2R RX | LowSpeed receive |
| 12,13,14 | GND | Ground |
| 15 | HS1TX+ | HighSpeed transmit 1 (positive) |
| 16 | HS1RX+ | HighSpeed receive 1 (positive) |
| 17 | HS1TX- | HighSpeed transmit 1 (negative) |
| 18 | HS1RX- | HighSpeed receive 1 (negative) |
| 19 | GND | Ground |
| 20 | DPPWR |
Power |
The Thunderbolt cable has five wires: one for management and two uni-directional pairs, one for incoming and second for outgoing traffic. The cable is a crossover cable, it swaps all receive and transmit lanes; e.g., HS1TX(P) of the source is connected to HS1RX(P) of the sink. As an active cable, it includes circuitry inside the connectors.

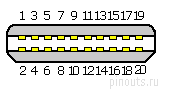

 правильная
правильная с ошибками
с ошибками